
BrainX adopts MOXO d-CPT (Introduced by Esperanza) in Hong Kong, which quantifies children’s attentive level rapidly and demonstrate benchmark on same aged peers comparison.

MOXO d-CPT is widely applied in hospitals & education institutions, and adapted in 39 countries as ADHD diagnostic tool. The assessment can be completed in 30 minutes quantifying children’s attentive level rapidly and demonstrating benchmark on same aged peers comparison.
Diagnosis reports provide an overall picture of your client’s performance throughout the assessment, including in the presence of auditory, visual and combined audio-visual distractors.
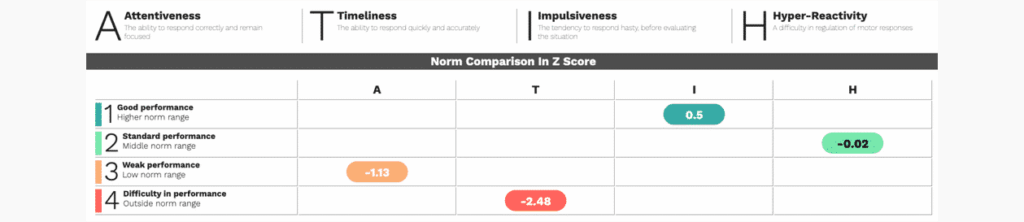
Standardized Z-scores are offered for four different attention metrics: Attentiveness, Timeliness, Hyper-Reactivity and Impulsiveness. Scores are standardized based on an age and gender-matched norm group.
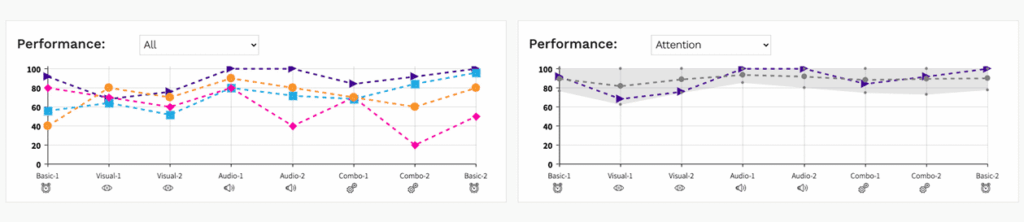
View your client’s performs throughout the assessment and with all distractor types, and interactively compare the different metrics side-by-side. For assessment takers 26 and younger, you can compare the individual’s performance to a general population reference group.
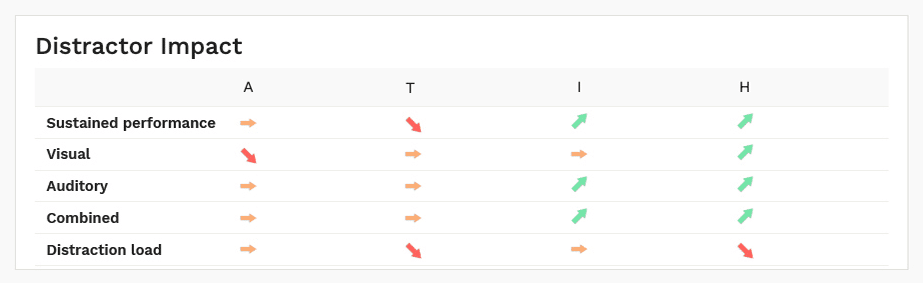
Clearly see which scenarios led to increased performance, and which conditions were more difficult for your client in the distractor impact graph.
*For Premium Report only
View your client’s standardized percentile scores to capture cognitive and executive functions throughout he entire assessment, and under visual or auditory distraction.
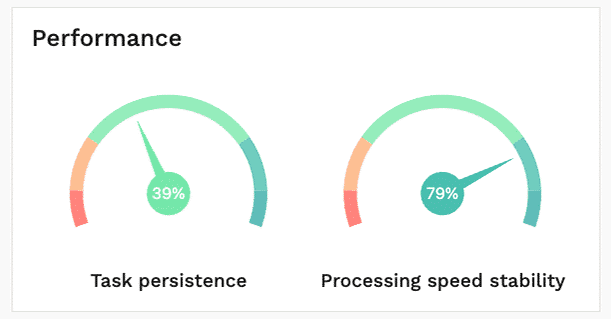
Understand general performance patterns over the entire assessment presented in standardized percentiles. Task Persistence measures the ability to remain focused over an extended period of time. Processing Speed Stability measures the ability to respond consistently over time.
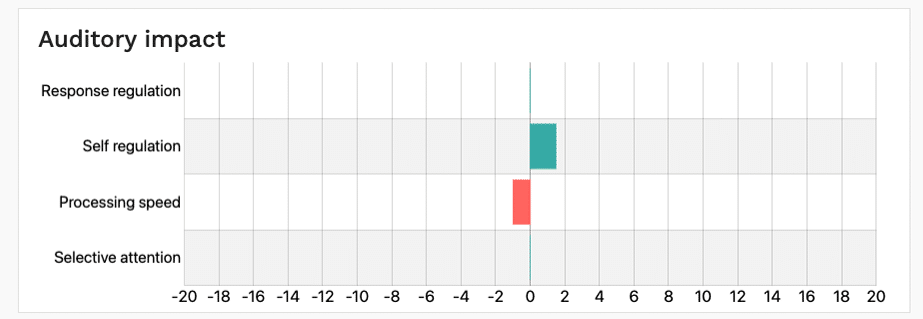
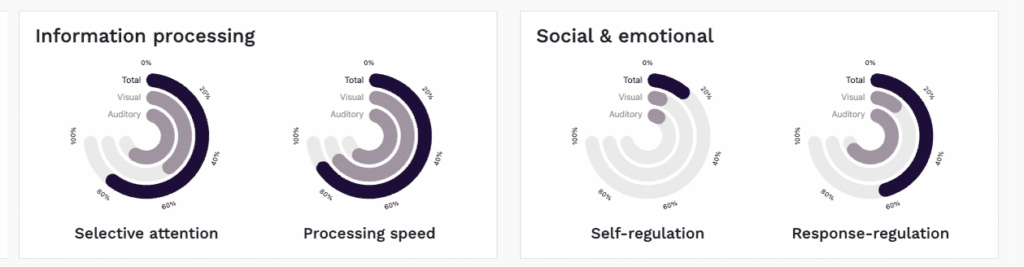
See the difference between your client’s selective attention, processing speed, response-regulation and self-regulation performance with auditory and visual distractors compared to their performance without any distractors.
The focus metric is an aggregate measure of basic attention abilities. This parameter provides a general representation of the individual’s attention ability, and comprises the average of selective attention, processing speed, self-regulation and response-regulation.
Auditory focus metric is an aggregate measure of basic attention abilities while auditory distractors are present. This parameter provides a general representation of the individual’s attention ability in the presence of auditory distraction, and comprises the average of selective attention, processing speed, self-regulation and response-regulation while auditory distractors are present.
Visual focus metric is an aggregate measure of basic attention abilities while visual
distractors are presented. This parameter provides a general representation of the individual’s attention ability in the presence of visual distraction, and comprises the average of selective attention, processing speed, self-regulation and response-regulation while visual distractors are present.
Selective Attention
Selective-attention measures the individual’s ability to respond correctly and remain focused throughout the entire MOXO assessment. This parameter reflects how often the individual correctly presses the response key when the target stimulus is presented.
Processing Speed
Processing speed measures the individual’s ability to respond quickly and accurately throughout the entire MOXO assessment. This parameter reflects how much time it takes the individual to press the response key when the target stimulus is presented.
Response-Regulation
Response-regulation measures the child’s ability to control how they respond. This parameter reflects how often the individual presses a response key when a response was not required. This includes more than one press after a target is presented, or key presses other than the response key.
Processing Speed Stability
Processing speed stability measures the ability to respond consistently over time. This parameter reflects the standard deviation of the individual’s processing speed throughout the assessment.
*For Premium Report only
MOXO highlights exclusive indicators for your attention and consideration. We offer three indicators that allow you to evaluate the validity, credibility and uniqueness of the assessment before diving into attention profiles and patterns.
![]()
The validity indicator assesses whether the individual’s responses were consistent and reliable. An invalid assessment indicates a likelihood of random pressing, regardless of the rules of the assessment.
![]()
The dissimilarity indicator showcases the uniqueness of an individual’s profile, highlighting how an individual profile stands out from the norm by intelligently considering the intricate web of relationships between attentional metrics. A dissimilar assessment suggests that the individual’s performance is very unique or unusual, possibly requiring special attention or investigation.
![]()
The malingering indicator measures whether the individual made a deliberate effort to fake attentional difficulties for personal benefits. High malingering scores are characterized by an excessively poor performance. In older adolescents and adults a positive malingering evaluation indicates that the participant may be intentionally faking a poor attentional performance. In children a positive malingering evaluation points to questions about their performance motivations and understanding of the task.